Lobe and Vane Pumps Overview
In different industries, lobe and vane pumps play pivotal roles as they are used for fluid transportation in processes that need consistency, accuracy, and long-lasting pumps. These two types of pumps have some basic components in common, but offer varying advantages based on the specific fluid, system, and operational conditions. In this blog we shall look at the differences between lobe and vane pumps and the applications where one or the other would be more beneficial, underscoring the fact that the right choice in pump can greatly enhance system efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Learning Outcomes for Vane and Lobe Pumps

Important industrial processes utilize a certain set of equipment. Some pieces of equipment are more necessary and important than others. Vane and lobe pumps are two of the most commonly utilized positive displacement pumps within various industries. With both types of pumps, there are rotary mechanisms that are used for the purpose of displacing liquid. The mechanism within these devices are different; however both of them accomplish the same goal of moving set amounts of liquid in a given period of time.
For most industries that deal with handling of fluids, the most important features when selecting between a lobe pump and a vane pump include viscosity of fluid, rotary torque outputs, hydraulic pressure, and the volumetric flow rates. Let us better understand how these pumps operate and in what situations they are most helpful.
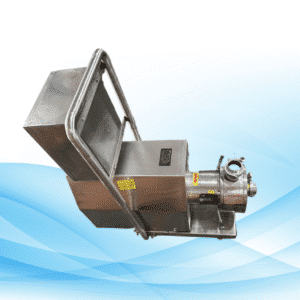
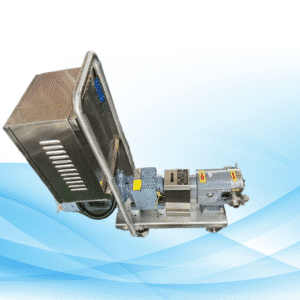
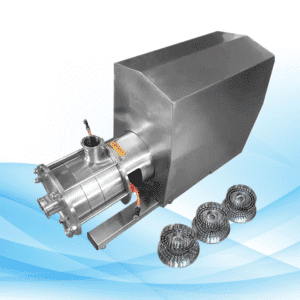
2. The Functionality of Lobe Pumps
Lobe pumps consist of two or more lobes that rotate in opposite directions with the fluid. As lobes rotate, fluid is captured in the pump between the lobes and housing, then expelled with the lobes’ movement. This fluid handling ensures smooth, steady flow with minimal pulsation.
Key Features of Lobe Pumps:
- Positive Displacement – Each rotation moves a fixed volume of fluid.
- Non-Contacting Lobes – Reduce wear and tear, increasing durability as the lobes don’t touch.
- Versatile – Designed to handle thin and thick fluids seamlessly.
Applications
Food and beverage, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries’ lobe pumps for moving viscous fluids and pastes.
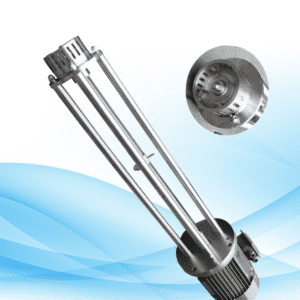
3. Operational Principles of Vane Pumps
In the case of vane pumps, they incorporate a rotor with movable blades or vanes, which are adjusted to slide in and out of their corresponding slots. With the rotation of the rotor, the vanes also rotate, ensuring they remain in contact with the casing. This results in the formation of chambers that change in volume and fluid is transferred from the inlet to the outlet. Vane pumps are preferred due to their self-priming abilities and large capacity to work with low viscosity fluids.
Other Important Characteristics of Vane Pumps Are:
- Self-Priming: Operates independently without help from other devices in order to start discharging fluid.
- Compact Design: Takes less space compared to other types of pumps.
- Variable Flow Rate: Managing pump speed allows changing the flow rate of the pump.
Uses:
Vane pumps are employed in systems that deal with high-pressure or high-flow applications, for example, in automotive, hydraulic systems, and air compressors.
4. Comparing Lobe With Vane Pumps
It is important to understand both lobe and vane pumps if you want to pick the right type for your uses. Below is a summary of the most important points regarding their differences:
| Feature | Lobe Pump | Vane Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Design | Two or more lobes rotating in opposite directions | Vanes sliding in a rotor cavity |
| Fluid Type | Suitable for high-viscosity and shear-sensitive fluids | Ideal for low to medium viscosity fluids |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency with minimal pulsation | Good efficiency but may have slight pulsation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to non-contacting lobes | Requires more maintenance due to moving vanes |
| Flow Characteristics | Smooth and consistent flow | Can have a variable flow depending on speed |
5. Uses Both Lobe And Vane Pumps
Both lobe and vane pumps are versatile, however, they can be more diverse based on specialized needs for a particular field.
Lobe Pumps:
- Food And Beverage: Carrying high viscosity items, for example, syrups, paste like substances and oils to ensure that there is no degradation on flavor or texture.
- Pharmaceutical: Best for accurate dosing of liquids that are sensitive and need high precision to avoid contamination or damage.
- Cosmetic Industry: Best used to transfer creams, lotions, and ointments while preserving its thickness and value.
Vane Pumps:
- Hydraulic Systems: Vane Pumps are largely employed for the movement of hydraulic fluids in mining and construction machinery.
- Automotive: They function in power steering and braking systems.
- Oil and Gas: Vane pumps are often employed for the transportation of oils and other fluids of lower viscosity in industrial applications.
6. Benefits of Using Lobe and Vane Pumps
Each type of these pumps have their pros which makes them fit to be used for a range of activities.
Lobe Pumps Benefits:
- Low Pulsation: Essential for processes like food manufacturing where smooth, continuous flow without interruption is critical.
- High Efficiency: Lobe pumps are very effective when dealing with highly viscous and shear-sensitive fluids.
- Flexibility: Can accept wide ranges of fluid viscosity without sustaining damage.
Vane Pumps Benefits:
- Self-Priming: Powerful for dependable use, since the vane pump can start on its own without needing assistance.
- Reduced Floor Space: Vane pumps smaller proportions are fitting in compacted areas.
- Reliability: Fewer moving components translate to decreased wear and longer operation periods.
7. Common Problems and Maintenance Suggestions
While lobe and vane pumps are dependable, they might face certain problems over a period of time. Knowing these problems and how to maintain your pumps can help to a greater extent in improving their overall efficiency.
For every problem there is a solution, let’s focus on lobe pumps deep down knowing that solutions to problems is what matters:
- Seal Leaks: It is undeniable that seals are susceptible to leakage due to extreme high pressures.
- Cavitation: Lobe pumps can also experience cavitation, which is the formation and collapsing of bubbles, if they are not properly designed and constructed.
Moving on to some common issues with vane pumps:
- Vane Wear: With passage of time, one can expect performance degradation when it comes to pumps, as the vanes are bound to wear down and lose its efficiency.
- Fluid Contamination: We can also refer to this problem as FOD: Foreign Object Damage, which illustrates that foreign elements like particles while fluid travels through the system can prove fatal.
Helpful Suggestions for Maintenance:
- Overseeing the condition of your seals and vanes.
- Applying filters for blocking particles from entering the system is a suggestion that seems too simple.
- Prevention is better than cure, so ensuring to frequently clean your pumps as prevention to fluid build up and contaminations.
8. Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The selection of a pump, either a lobe or a vane, is determined by many factors such as fluid type, flow rate, and the operating environment. Both lobe and vane pumps seem to serve distinct functions and are irreplaceable for handling fluids with accuracy and precision in specific industrial sectors. With the knowledge of the differences of each type of these pumps, it is easier to select one that best suits your needs.
In case you are looking for an effective and dependable pump for viscous fluids, a lobe pump would serve you best. For more compact needs, like automotive or hydraulic systems, self-priming vane pumps would serve you best.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between a lobe pump and a vane pump?
The design and operation of both types dictate the defining difference. Lobe pumps rotate lobes to move fluid, while vane pumps utilize sliding vanes mounted on a rotor. This makes lobe pumps less efficient for high viscosity fluids, while vane pumps for self-priming compact units.
2. What pump works best with high-viscosity fluids?
Pastes, syrups, and creams are high viscosity fluids that lobe pumps work best with. These rotary positive displacement pumps are specially designed to reduce shear and maintain smooth, uniform flow.
3. Are vane pumps suitable for high-pressure applications?
Hydraulic systems and air compressors often make use of vane pumps as they can work under moderate to high pressure, allowing the pumps to function efficiently.
4. What are the maintenance procedures for lobe or vane pumps?
Routine maintenance comprises checking the seals, ensuring there are no leaks, maintaining proper lubrication, and overhauling worn parts like vanes or lobes. The lobe or vane pumps also need to be cleaned, while filters should be used to maintain the cleanliness of the system and limit contaminating debris.
5. In which sectors are lobe and vane pumps used?
While vane pumps are especially popular in the automotive and oil and gas industries, as well as in hydraulic systems, lobe pumps are prominent in food processing and cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries.