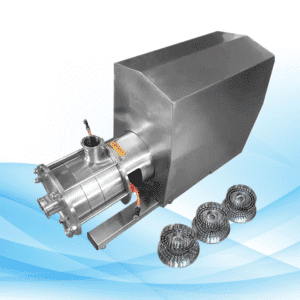
Introduction
Lobe pumps also known as positive displacement pumps are very handy in many applications, especially in the areas of transferring sensitive fluids because they do not harm the fluids. These types of pumps also work with rotating lobes that serve to transfer liquids and allow providing a negligible variation of the out coming flow rate, which makes these pumps rather effective and accurate. So understanding the engineering intricacies of lobe pumps can improve their use in quite a number of industries like food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, chemical processing among others. This blog will explore how to define, operate, apply, advantages, and also maintain lobe pumps and their role in today’s industry.
What is Lobe Pumps?

Definition and Basic Structure
In sections II and III, cite some applications of prosthetic devices and write what they represent as. Flow, lobe pump is entirely occupied by sweeping two or more rotating lobes that pull the surrounding fluid in by a vacuum and forces this fluid out through an outlet. They operate in agreement to ensure the uninterrupted movement of the material. To begin with, the basic components of Lobe pumps can be highlighted. They include:
- Lobes: The part of the lobe pump responsible for the suction and discharge.
- Casing: This is the outer wrap of the lobe structure, meant to support pressure.
- Drive Mechanism: This is such as electric motor which has a driving mechanical action on the lobes. It deals with seals and bearings which prevent loss of fluid and leakage respectively.
Using Lobe Pumps
Although there are other types of Lobe Pumps, the most commonly used ones are:
- External Lobe Pumps: These are defined as Lobe Pumps having their lobes external to the pump casing and have high flow rates.
- Internal Lobe Pumps: These Lobe Pumps have their lobes rotating within the pump casing, and this affects their capacity to create high pump pressures.
How Lobe Pumps Work

Working Principle
The major operating principle of a lobe pump is long and straight forward. Fans rotate and form void space which fills with liquid. In extending the lobes’ rotation, liquid is discharged via the liquid outlet. This positive displacement technique ensures accurate flow rates regardless of any increase/decrease in pressure within the system.
Flow Characteristics
Lobe pumps sensitive fluids can be effectively operated without the effects of pulsation in the flow. Their capacity to sustain flow stability is an asset under many applications.
Applications of Lobe Pumps
Industrial Applications
In the Food and Beverage Sector, lobe pumps are used in the food and beverage industry for pumping out candies, and flavors, as well as other delicate products. The flow aid is designed to minimize contamination and aid the constant flow of rates.
In the Pharmaceutical Industry, lobe scanners find numerous applications in the pharmaceutical industry that demands both efficiency and hygiene. They are applied in the movement of vaccines, syrups, and other compounds to the markets under strict pharmaceutical regulations.
Other Applications:
- Processing of chemicals: In chemical processing, lobe pumps are used for pumping thick and dangerous fluids. They are built strong enough to handle different types of fluids, making them the best in the industry.
- Wastewater treatment: Lobe pumps are worth mention also when engaging in facilities where waste water treatment is being carried out, core reason being the movement of sludge and other lighting viscous materials cut down on cost on the wider picture.
Efficiency and Reliability
One of the most ample advantages of lobe pumps is their efficiency. They have the ability to have some fixed flow rates, which increases reliability over a number of scenarios. Such reliability means that there is less downtime and productivity levels increase.
Versatility in Handling Fluids
Lobe pumps are also very versatile in that they can pump different fluids, including those that are thick or have abrasive particles. This means that these pumps can be used in various industries.
Limitations and Challenges
Cost Considerations
Although these lobe pumps have their merits, lobe pumps are in most cases pricier than others. The economies of scale in capital investment and the subsequent installation cost may put off some users, especially for small size operations.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is also imperative for lobe pumps to perform up to expectation. The seals, bearings, and lobes should be inspected and replaced routinely for them to work cost effectively, which adds to the running costs.
Maintenance and Care
Routine Maintenance Practices
Inspection and Cleaning: To secure the future of the pumps, lobe pumps need to be inspected and cleaned regularly. All the same, operators need to take note of any worn out parts as well as leakage and blockages to pump in the most correct way without straining the pump.
Lubrication and Parts Replacement: To avoid damage from friction, there is need to apply grease to the moving parts of a pump. In addition, timely bearing and sealing material replacement will allow extending of pump apparatus life span.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying Problems
Common lobe pump malfunctions include a decrease in the flow rate, abnormal sounds and encountered leaks. Identifying these problems early can lead to bigger consequences being averted.
Solutions and Repairs
In order to fix some of the basic problems, operators can carry out some simple repairs, for example, placement of readily available options such as tightening of some connections, installing new parts, and changing the speed of the pump.
Conclusion
In conclusion, people working with the fluid transfer industry will find it essential to comprehend lobe pumps. Their design and the efficiency in operation allows them to be used across different fields from food production to chemical industries. Permanent placement of lobe pumps in some of the relevant applications will enable most organizations to improve their operational efficiency and maintain quality of processes. As the technicalities of the lobe pumps are appreciated, so will the management of fluid operations be more effective, resulting in better outcomes.