Harnessing Full Possible Advantages of Positive Displacement Pumps
Harnessing full possible advantages of positive displacement pumps can raise performance level in various industries considerably. As these pumps are versatile and can work with different kinds of fluids, they are favored in industries such as oil and gas, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals.
In this detailed article, we will cover all important aspects of positive displacement pumps: their definition, classification, working mechanisms, components, calculation of efficiency, application, merits, maintenance, and staff safety. Additionally, we’ll explain the characteristics of both positive and non-positive displacement pumps and the reasons why they are predominantly and only used where they are.

A Brief Overview of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps are those pumps that are used to displace a given volume of fluid in a mechanically structured device, in one direction without letting any fluid reverse back. These are most popular when there is a need for a constant rate of flow and viscous fluids are being pumped.
Such pumps encapsulate fluid and impel a set portion of the trapped fluid into the discharge outlet. This is an advantageous property since it means that variations in the pressure can still be tolerated.
Positive vs Non-Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive and non–positive displacement pumps differ from one another in the principles of operation employed in moving fluids. Positive displacement pumps deal with a set amount of fluid in a fixed volume measure, irrespective of what the pressure state is.
They are thus quite well suited for handling viscous fluids, or tend to be useful where there is the need for a steady flow. Positive displacement pumps work efficiently, but non-positive displacement pumps like centrifugal ones cannot operate under pressure. These types cannot be used for pressure application since pressure can either burst or alter the output flow.
It is important to appreciate the difference between these two types of pumps, especially when specific tasks call for a right pump.
Standard Principle of a Positive Displacement Pump
Positive displacement pumps operate on a simple principle – liquid is captured in a volume and then moved by the force of the liquid through an outlet. Sometimes two-thirds of the crank revolution provides suction and the remaining third is used for the ejection.
There are two major subdivisions of positive displacement pumps:
Rotary Positive Displacement Pumps
Rotary positive displacement pumps include Gear, Lobe, and Vane pumps. In this type of pumping, a rotating part has the capacity of entraining and transporting fluid. Rotation of the fluid is either by movement of the gears or the vanes, which makes such pumps very appropriate for viscous fluids.
Reciprocating Positive Displacement Pumps
The second type of positive displacement pump is the reciprocating ones. In this case, the fluid is displaced back and forth by a diaphragm or piston or cylinder. Such pumps include dynamic pumps, plunger pumps, and diaphragm pumps. These pumps are preferable for continuous applications which require the use of a specific fluid volume.
Key Components of Positive Displacement Pumps
The action and usefulness of these pumps depend on understanding the structural components:
Pump Housing
This is the outer protection which contains the machine moving parts and guides the fluid.
Inlet and Outlet Ports
The inlet is used to accept fluid and the outlet to release the pump fluid.
Gears, Lobes, Pistons, or Diaphragms
Depending on the category of positive displacement pump, these parts encase and move the fluid.
Valves
They are used to control the movement of the fluid inside the pump, more so in piston pumps.
Each component has its own importance with reference to pumping activity.
Essential Functions of Positive Displacement Pumps
Different positive displacement pumps operate in their own functional characteristics and vary with their application.
Gear Pumps
It is used for thick fluids like oils where fluid movement is performed using fixed rotation gears.
Lobe Pumps
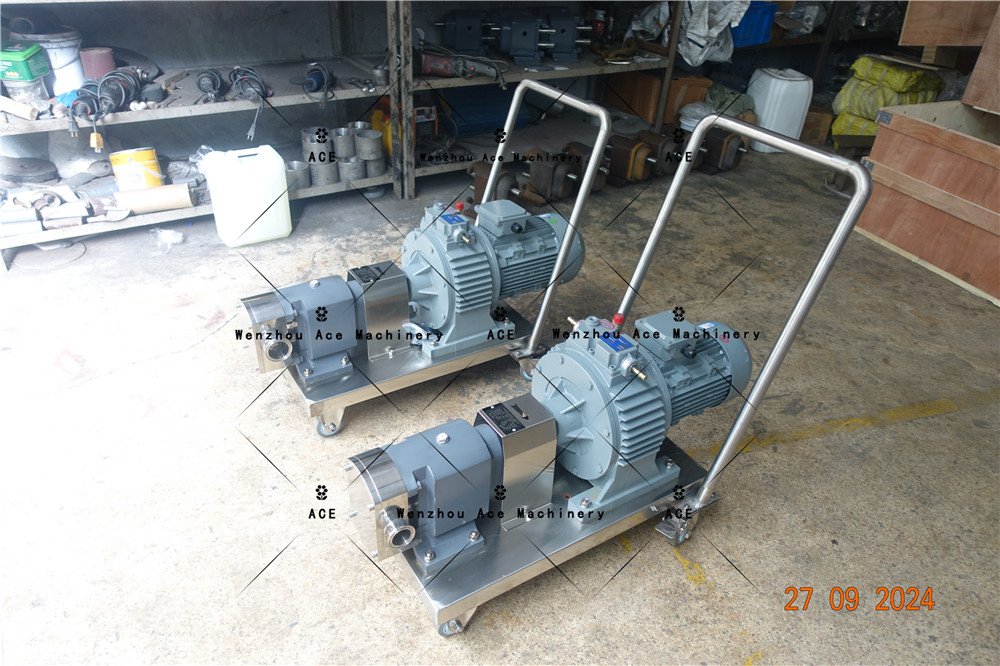

These pumps, normally employed in food processing industries, cater to high viscosity fluids without destroying them.
Vane Pumps
These pumps incorporate vanes to sweep fluids, which are integrated mainly in automotive and air conditioning systems.
Piston Pumps
These are accepted for their pressure generation when pushing water systems due to their use of a piston, which in turn makes them work on fluids.
Diaphragm Pumps
This is used in chemical industries for highly corrosive or abrasive fluids and is very effective in operation.
Efficiency Calculation for Positive Displacement Pumps
The pump probably is the most critical driving component which determines.
Positive displacement pump efficiency involves the consideration of two important factors: volumetric efficiency and mechanical efficiency.
Volumetric Efficiency
This aims at how effective the pump is in pumping out the expected volume of a liquid as compared to the theoretical volume of a fluid, which is always estimated. Its determination is by measuring the actual flow rate against the expected one.
[Volumetric Efficiency = (Actual Flow Rate / Theoretical Flow Rate) x 100]
Above is the general and mathematical analysis of volumetric efficiency.
Applications of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps are various and as well as application with regard to the different fluids they pump. Below are some of the applications:
Oil and Gas
The use of positive displacement pumps is enabling, especially in pumping crude oil from offshore platforms where there is a need to maintain high pressures and flow rates.
Pharmaceuticals
In this field, accurate work is paramount, and here it is not different as well. Diaphragm and peristaltic pumps are deployable for pumping articles of sensitive or sterile nature.
Food and Beverage
These pumps are used for heavy viscous throw and particulate matter-filled liquids like sauces, syrups, etc.
Chemical Processing
Transfer of hazardous liquids in process industries is done economically using positive displacement pumps. These pumps are highly appreciated for their accuracy and efficiency, and operation with difficult fluids in difficult conditions.
Maintenance of Positive Displacement Pumps
Proper maintenance of positive displacement pumps enhances their effectiveness and reliability over time. Here are some basic maintenance steps that should be kept in mind:
Regular Inspection
Regular examinations of the components of the pump such as seals, valves, and bearings assist in preventing unnecessary wear and tear of the parts.
Lubrication
Moving components, particularly in rotary pumps, should be lubricated to prevent the rubbing of the parts that may lead to a short lifespan of the pump.
Check for Leaks
A leak in a system indicates that certain components, particularly seals and gaskets, have worn out. Rapid response to such leaking fluids will reduce further damage to the facility.
Monitor Flow Rates
When there are drastic or long-duration changes in flow rates, sudden abnormalities arise, and this may be due to an obstruction or breakdown in the pump.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
It is essential to follow the maintenance program and recommendations issued by the producer of the pumps dealing with positive displacement. Following these measures will help in enhancing the lifespan and efficiency of your pumps, thus less downtime and reduction of operational expenses.
Safety Guidelines
Safety and security must always be considered of utmost importance whenever positive displacement pumps are in use. Here are some key safety measures:
Safety and Reassurance
All operators should be given proper training on pump operation and its maintenance.
Preventions
Employing pressure-relieving devices to avoid system overpressure, which can cause loss or dangerous scenarios for people and equipment.
Protective Clothing
Suitable clothing for hazardous and/or corrosive fluids should be worn at all times.
Stand-by Operating Procedures
Proper ‘shut down’ procedures should exist to restrain damage as a result of quick stops or a blackout.
Preventive Measures
Maintenance includes the practice of regular assessment of the pumping apparatus for any forms of hazards and or safety risks to eliminate them. While performing the above actions, it is important to note that implementation of all these practices not only saves the machinery but also the workers.
Conclusion
Positive displacement pumps have a lot of uses and, in fact, can make one’s life easier in many ways. Learning the workings of positive displacement pumps, their types, efficiency evaluation, and areas of application can enable one to make full use of them. Maintenance and safety practices ensure that they are efficient and long-lasting.
Hence, whether you are looking for a comparison of positive and non-positive displacement pumps or wondering how to make the best of your existing systems, this detailed guide